Forms a Virtual Image That Is Located Behind the Mirror
A virtual image formed by a concave mirror is always enlarged. As shown in the diagram below the virtual image appears the same distance behind the plane mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
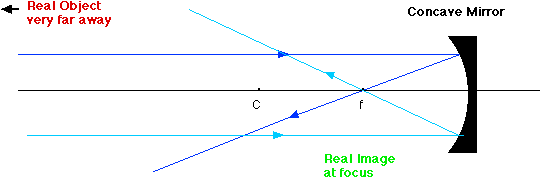
Image Formation By Mirrors Physics
What is the magnification of the image.
. A _____ mirror always forms a virtual image. With a plane mirror the image may be infinitely far behind the mirror depending on where the object is located in front of the mirror. State three characteristics of the image.
For instance rays emanating from the tip of the object appear after reflection from the mirror to come from a point which is behind the mirror. The focal length f and the image distance are always NEGATIVE beacause the image is formed behind the mirror. A virtual image is always located behind the optic lens or mirror that creates it.
The image produced by a convex mirror is always closer to the mirror than it would be in a plane mirror for the same object distance. Figure 72 shows what happens when the object distance is less than the focal length In this case the image appears to an observer looking straight at the mirror to be located behind the mirror. Image length is half the radius of curvature.
A concave mirror always forms a virtual image of a real object. Identify the mirror used when an object is placed between infinity and the device the image formed is virtual erect diminished between pole and focus and behind it. When an object is placed 220 cm in front of a convex spherical mirror a virtual image forms 145 cm behind the mirror.
They are also located behind the mirror. Virtual images are always located behind the mirror. Plane mirrors and convex mirrors form virtual images.
Virtual images are not real. All you really need to know is that the image formed by the first mirror regardless of whether its real or virtual become the. An object 4 cm in size is placed at 25 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm.
The reflected rays are obtained by using the law of reflection. Determine the mirrors focal length in cm and the magnification. A diverging mirror always forms a _____ image.
The characteristics of an image formed by a flat mirror are. They are always the same size as the object Concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images. If the image formed by mirror 1 is in front of mirror 2 the object is real.
Repeating this process for point gives the image point. An object located 18 cm from a convex mirror produces a virtual image 9 cm from the mirror. If its behind the object is virtual.
Thus you could never see them when sighting in a mirror. They can be upright if virtual or inverted if real. Virtual images formed by _____ always are located behind the mirror.
Note that only two rays are used to locate for. For an object in front of a single convex mirror what is the greatest distance behind the mirror at which the image can be found. When an object is placed 275 cm in front of a convex spherical mirror a virtual image forms 115 cm behind the mirror.
Virtual images can be magnified in size reduced in size or the same size as the object. You cant touch the virtual image or put your hand in the pattern of light that you seem to see. When the object of a concave mirror is inside the focal point the image is virtual.
Magnification m v u 15 -5 3. A convex mirror forms smaller upright and virtual images. Your right eye appears as the left eye in your image etc.
The image is a virtual and upright image. He notices that his image appears to be 060 m tall. A The image and object are the same distance from the mirror b The image is a virtual image and c The image is situated behind the mirror.
Fun House A boy is standing near a convex mirror in a fun house at a fair. A the mirrors focal length in cm b the magnification. All you care about is where the image forms in relation to mirror 2.
The nature of image formed by an object placed in front of a convex mirror is always diminished virtual and erect. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for an object beyond its center of curvature. Previously in this lesson ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the location size orientation and type of image formed by concave mirrors.
Virtual images formed by mirrors always are located _____ the mirror. Thus the image formed is virtual erect and magnified by a factor of 3. Frankly Im not sure how useful this concept of a virtual object is.
They can be behind the mirror if virtual or in front of the mirror if real. Virtual images can be formed by concave convex and plane mirrors. Thus a virtual and erect image is formed at 15 cm behind the mirror.
If the magnification of the mirror is 1 3 what. Virtual images can be either upright or inverted. Virtual _____ images formed by mirrors always are located behind the mirror.
The ray diagram constructed earlier for a convex mirror revealed that the image of the object was virtual upright reduced in size and located behind the mirror. Two light rays originating from point P on an object are reflected by a flat mirror into the eye of an observer. Thus when you look into a magnifying glass eyepiece or a make-up mirror you see light that appears to come from beyond the optic that creates the image.
V irtual images located behind the mirror have negative image distances by the sign convention of T able 231. Given f -330cm v -190cm. Different mirrors form different types of images.
M d d o i 1 8 9 c c m m 05 63. The image formed by a plane mirror is erect virtual the same size as the object and is located as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. Determine the mirrors focal length in cm and the magnification.
A concave mirror forms inverted real images of real objects located outside the focal point p f and upright magniÞ ed virtual images of real objects located inside the focal point p f of the mirror. Because the image is formed by a direct projection through the mirror it is reversed eg. Plane mirrors always produce virtual images which are upright and located behind the mirror.
Extending these reflected rays backward they seem to come from point Q behind the mirror which is where the virtual image is located. Virtual images result when the. A virtual image as opposed to a real image is produced by an optical system a combination of lenses andor mirrors when light rays from a source do not cross to form an image.
They can also be enlarged reduced or the same size as object. HINT a the mirrors focal length in cm 4253 x cm b the magnification 066 Need Help.
Physics Tutorial Ray Diagrams Concave Mirrors
Charles Wheatstone Mirror Stereoscope Xixc Stereoscope Wikipedia The Free Stereoscopic Virtual Reality Technology Digital Artists

Physics Tutorial Ray Diagrams Convex Mirrors Physics Tutorial Convex Mirror Mirrors And Lenses
Image Formation By Mirrors Physics
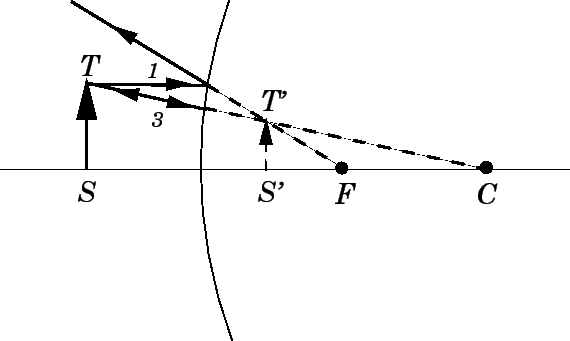
Image Formation By Convex Mirrors
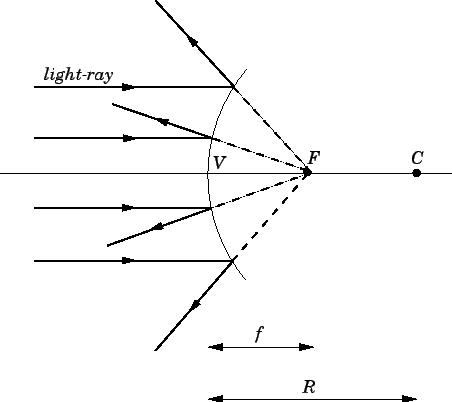
Image Formation By Convex Mirrors

Does A Convex Mirror Make Things Bigger In 2021 Convex Mirror Curved Mirror Mirror
Image Formation By Mirrors Physics

When The Object Is Between P And F Reflection And Refraction Light Reflection And Refraction Focus Images

Image Characteristics For Convex Mirrors Physics Tutorial Convex Mirror Physics
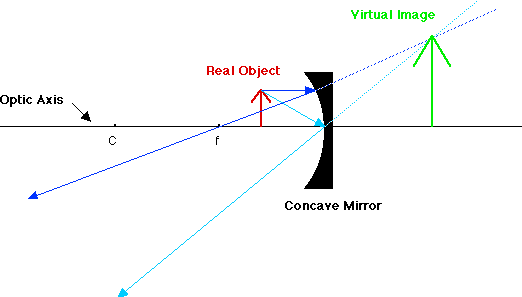



Comments
Post a Comment